Abstract
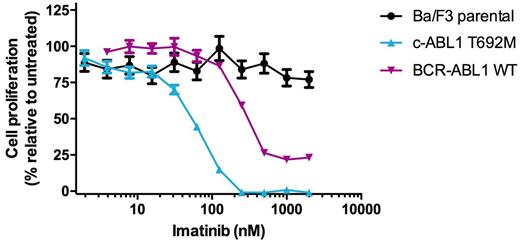
The use of ABL1 tyrosine kinase inhibitors has significantly improved outcomes for patients with chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) and Philadelphia chromosome (Ph)-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), which are driven by the constitutively activated BCR-ABL1 oncogenic fusion protein. More recently, additional mechanisms of ABL1 kinase activation have been reported in patients with Ph-like ALL (Roberts et al., NEJM 2014). However, a broader survey of the potential presence of activating ABL1 kinase mutations among a variety of other Ph-negative malignancies has yet to be explored. To better understand the scope and identity of c-ABL1 mutations in Ph-negative neoplasms, we screened a cohort of 182 primary patient specimens representing a range of Ph-negative leukemias (97 acute myeloid leukemia (AML), 47 Ph-negative ALL, 16 chronic myelomonocytic leukemia (CMML), 2 atypical CML, one juvenile myelomonocytic leukemia (JMML) and normal control) by isolating genomic DNA from mononuclear cells and completing targeted deep sequencing using a custom capture panel on the Illumina GAIIx sequencer. Between this cohort and the existing reported TCGA AML dataset, we identified subsets of patients with AML (3.8% in our cohort, ~3.5% in TCGA AML), CMML (1%), and Ph-negative ALL (2%) that harbor point mutations in the ABL1 kinase. Nearly all of these mutations occurred in the C-terminal portion of the kinase. A subset of these mutations demonstrate the capacity to transform Ba/F3 cells to IL-3-independent growth, and remain highly sensitive to clinically approved ABL1 tyrosine kinase inhibitors in cellular proliferation studies in vitro . Importantly, there was no detectable evidence of BCR-ABL1 transcripts by PCR in these patients, confirming their acquisition in c-ABL1. For example, an ABL1 T692M mutation was detected in a 54 y.o. male diagnosed with AML who also harbored an inv(16) by cytogenetic analysis but was negative for FLT3 , NPM1 , DNMT3A , and KIT mutations. Ba/F3 ABL1T692M cells rapidly grew out in the absence of IL-3 and were potently inhibited by imatinib (IC50: 53.1 nM). In total, our findings suggest that novel activating mutations of c-ABL1 are present at low but meaningful frequencies in Ph-negative leukemias and may represent actionable biomarkers for targeted therapy with ABL1 kinase inhibitors either alone or in combination with standard-of-care chemotherapy regimens.
Tyner: Leap Oncology: Consultancy; AstraZeneca: Research Funding; Janssen Pharmaceutica: Research Funding; Takeda Pharmaceutical Company: Research Funding; Gilead: Research Funding; Seattle Genetics: Research Funding; Syros: Research Funding; Genentech: Research Funding; Aptose Biosciences: Research Funding; Incyte Corporation: Research Funding; Agios Pharmaceuticals: Research Funding; Array Biopharma: Research Funding; Constellation Pharmaceuticals: Research Funding. Druker: Beta Cat: Equity Ownership, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Aptose Biosciences: Consultancy, Equity Ownership, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; McGraw Hill: Patents & Royalties; ARIAD: Research Funding; The Leukemia & Lymphoma Society: Other: Joint Steering Committee of AML Master Protocol, Research Funding; Blueprint Medicines: Consultancy, Equity Ownership, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; MolecularMD: Consultancy, Equity Ownership, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; GRAIL: Equity Ownership, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Roche TCRC: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Oregon Health & Science University: Patents & Royalties: #843 Mutated ABL Kinase Domains (licensed to various companies); #0996 Detection of Gleevec Resistant Mutations (licensed to various companies, including MolecularMD); #0606 Treatment of Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors (exclusively licensed to Novartis); Henry Stewart Talks: Patents & Royalties; Third Coast Therapeutics: Equity Ownership, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Baxalta US Inc.: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Novartis: Research Funding; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Research Funding; Cylene: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; MED-C: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; CTI Biopharma: Consultancy, Equity Ownership, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Gilead: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Monojul: Consultancy; Millipore: Patents & Royalties: Royalties from Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, which has an exclusive commercial license with Millipore for monoclonal antiphosphotyrosine antibody 4G10, which I developed while employed at DFCI.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal